Spatial multi-omics analysis has rapidly gained prominence in bioscience research. This technique supports the comprehensive analysis of multiple molecular data types, such as transcriptome, proteome and metabolome within their native spatial context in tissues (1). Such analysis also enables one to study the spatial organization and interactions of cells within tissues, providing a more detailed understanding of cellular heterogeneity and tissue microenvironments (2).
Scientific and translational use cases:
- Concurrent analysis of multiple molecular features in the same tissue section (or adjacent tissue sections).
- Provides spatial information, enabling the study of cellular interactions and tissue architecture.
- The high resolution can resolve individual molecules at subcellular levels.
- Study the effect of therapies on cell morphology, tissues and expression of markers
Transcriptomics focused spatial omics technologies are based on either sequencing or imaging platforms. Prominent sequencing based spatial analysis approaches include Visium (10X) and CosMX (Nanostring/Bruker), while Xenium (10X) and GeoMX (Nanostring/Bruker) are based on imaging. In addition to transcriptomics, these approaches combine imaging for protein expression and cell delineation, resulting in a multi-omics output.
🧬 Comparison Table: Transcript Capacity, Resolution and Applications
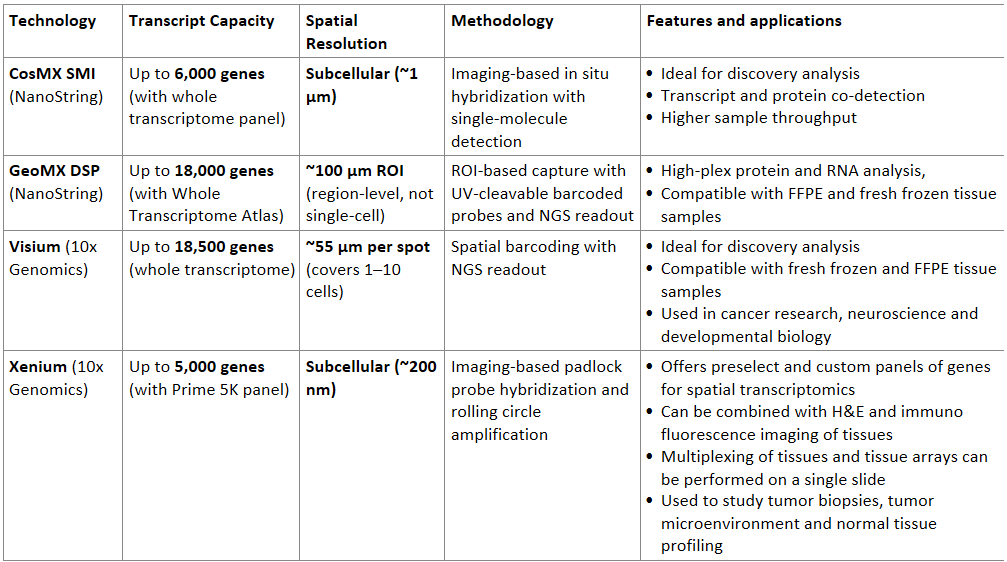
Table: The table compares popular multi-omics platforms based on their technology, features and applications
Despite all the complexities associated with such techniques, they are opening new avenues of research by connecting alteration of transcriptomics and proteomic changes with the cell typing, cell-cell interactions and pathophysiology of the tissue.
In the following posts I will delve into the applications of spatial multi-omics and bioinformatics approaches to analyze and interpret such datasets.
References
- Park J et al, Genome Biology volume 23, Article number: 256 (2022)
- Keissling P et al, Genome Medicine volume 16, Article number: 14 (2024)
- Spatial genomics to study tumor evolution and sub clone Spatial genomics maps the structure, nature and evolution of cancer clones | Nature
- 10X Genomics: Visium Spatial Gene Expression https://www.10xgenomics.com/platforms/visium
- NanoString Technologies: GeoMx Digital Spatial Profiler https://nanostring.com/products/geomx-digital-spatial-profiler/geomx-dsp-overview/
